Nashville's Premier Mental Health Treatment Programs
Nationally recognized in treating mental health & dual diagnosis disorders for a true path to healing & wellness.

Expert, Psychiatric Mental Health Treatment In NAshville, TN
At Arbor Wellness, our luxury mental health treatment center in Nashville aims to make the process of getting help easy. We incorporate evidence-based treatment modalities backed by a trauma-informed clinical philosophy.
We believe that healing is a journey, not to be defined by failure or success, but a process focused on overall wellness and self-respect.
Our mental health programs are rooted in the belief that no two clients are alike. We’re committed to transforming the landscape of mental health treatment, including your experience with it.
Request A Confidential Callback
A Continuum of Mental Health Treatment in Nashville, Tennessee
From residential treatment in a structured therapeutic environment to day treatment programs, our compassionate care team at Arbor Wellness works collaboratively to address the core issues impacting your emotional and mental health.

DETOX
At Arbor Wellness, our detox programs in Nashville, Tennessee help clients who are struggling with dual diagnosis disorders the proper treatment and medical supervision needed to successfully withdrawal from substances.
Detox

Residential Treatment
Mental health residential treatment centers in Tennessee, also called RTC or residential treatment facilities, are places where people who are dealing with a mental health condition can go to get the help that they need to get better.
Residential Treatment

INTENSIVE OUTPATIENT PROGRAM (IOP)
At Arbor Wellness, our Intensive outpatient programs, or IOPs, help people who are struggling to manage the symptoms of mental health conditions by providing them with...
Intensive Outpatient Program (IOP)

PARTIAL HOSPITALIZATION PROGRAM (PHP)
Partial Hospitalization Programs (PHP) are mental health treatment programs that provide a highly structured level of care but allow clients to return to housing offsite once clinical programming has ended for the day.
Partial Hospitalization Program (PHP)
PSYCHIATRY
At Arbor Wellness, our residential treatment programs offer Nashville psychiatry, staffed by extensively trained psychiatric professionals and other therapists.
Our programs provide compassionate, expert care that allows you to grow and become more confident.
Psychiatry
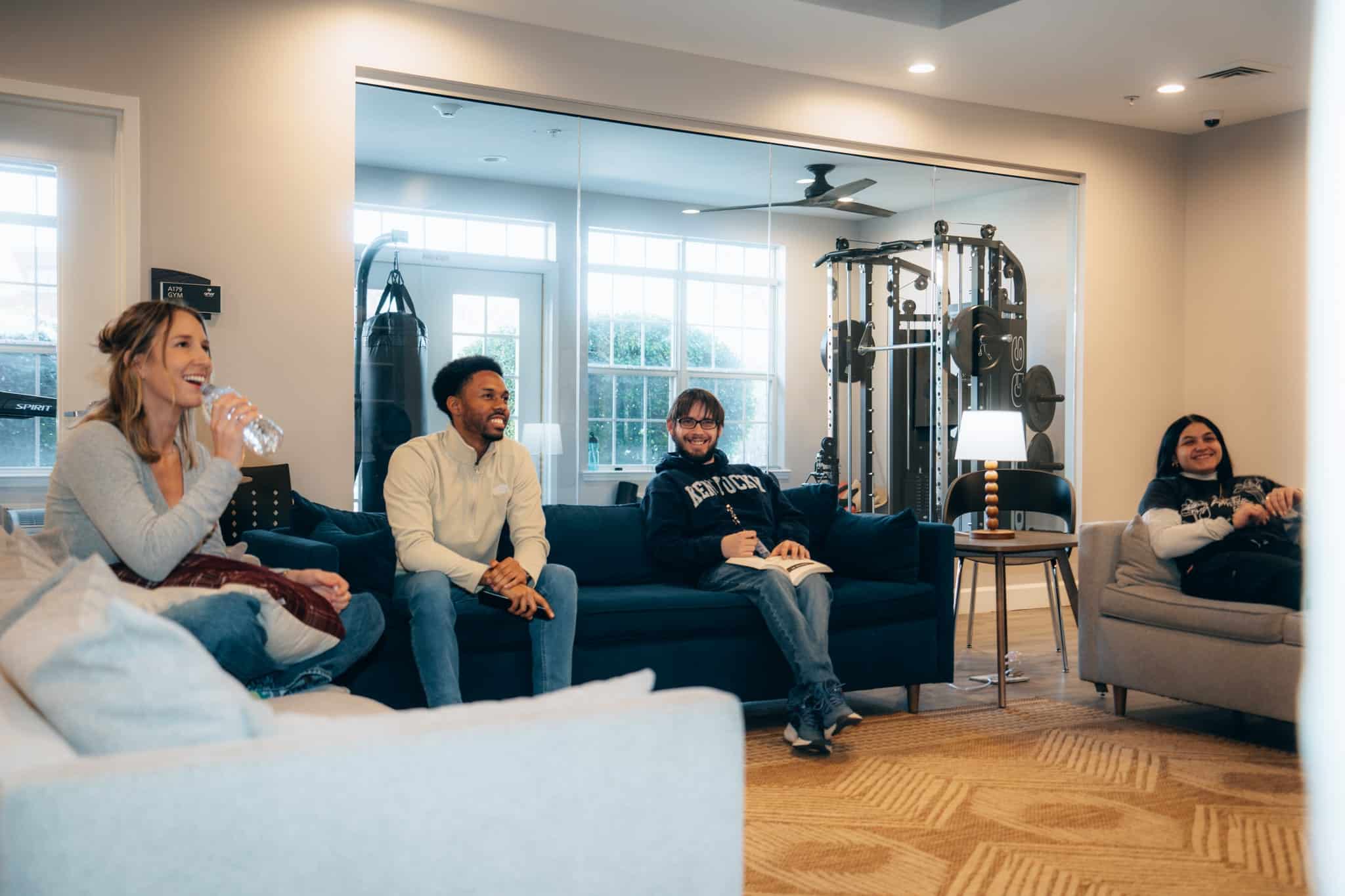
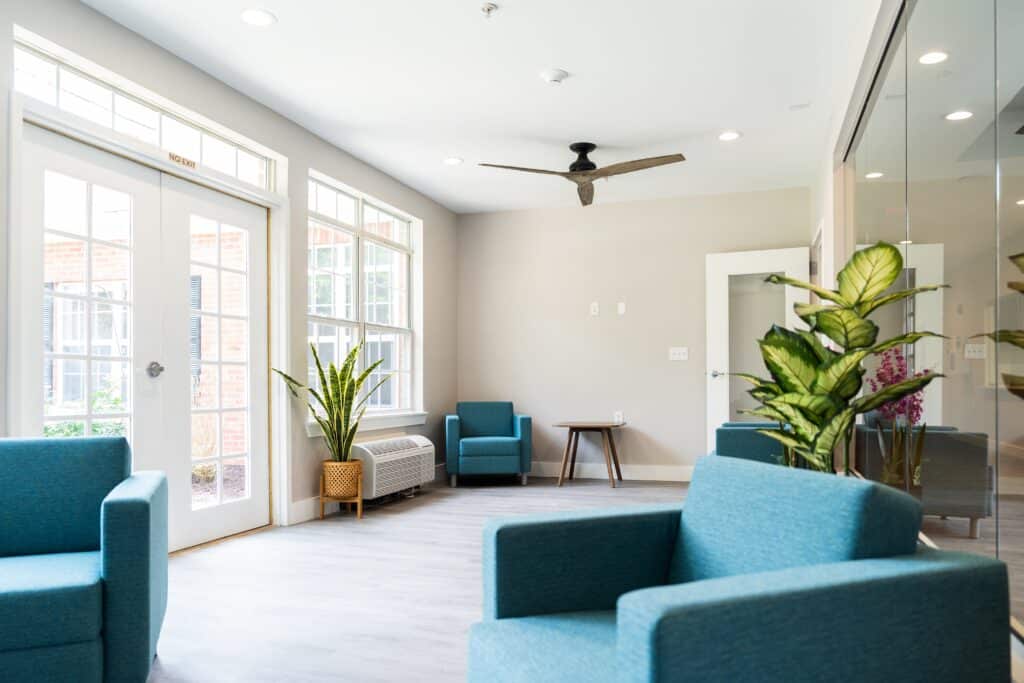
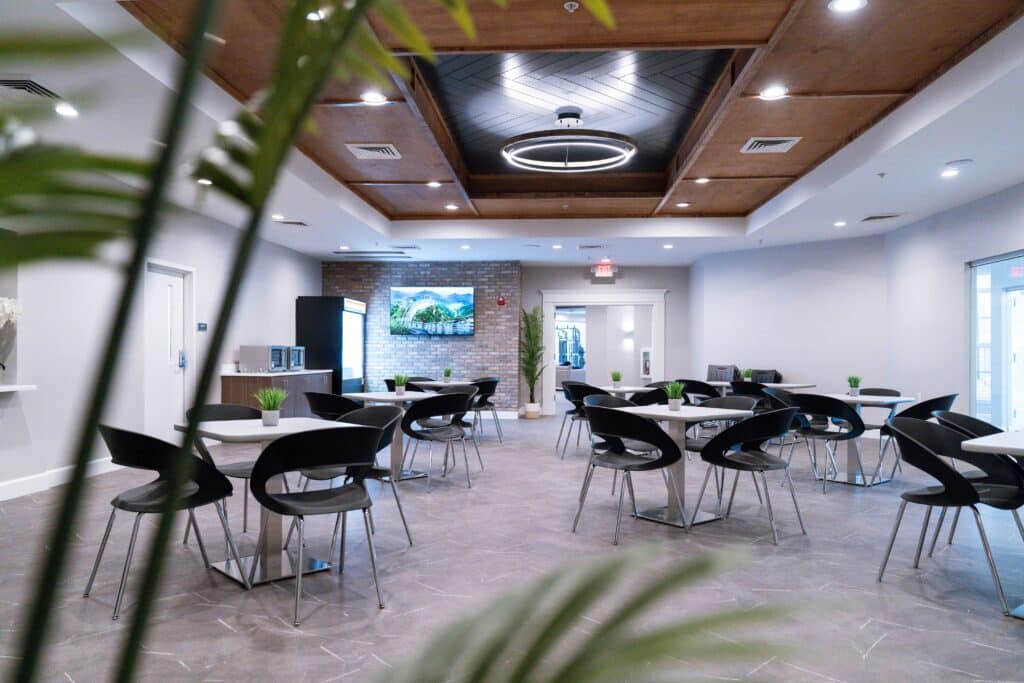
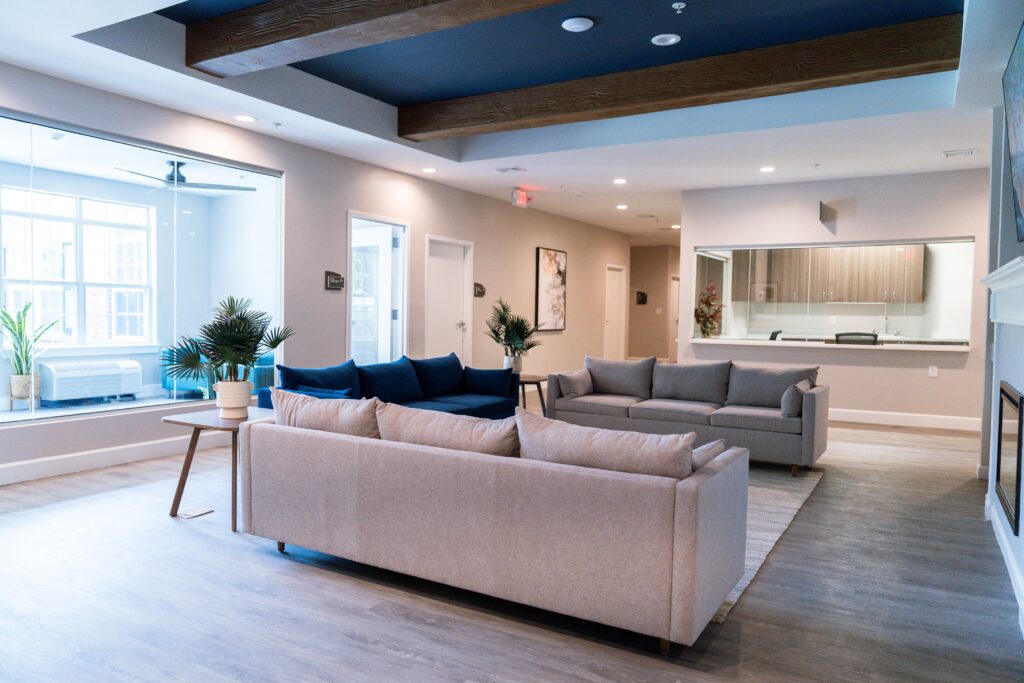
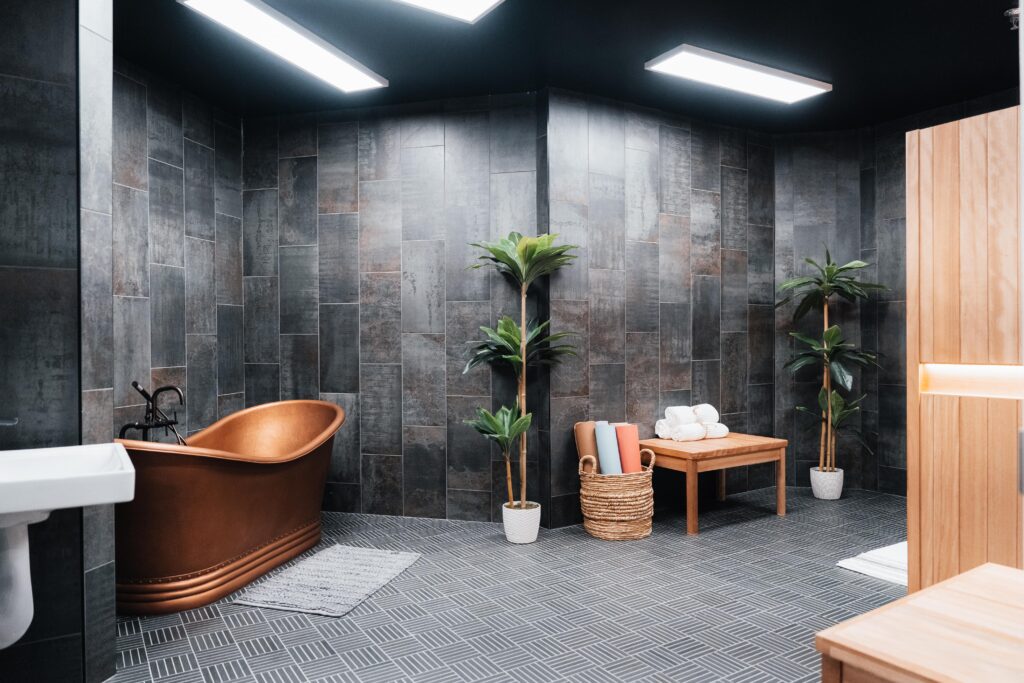
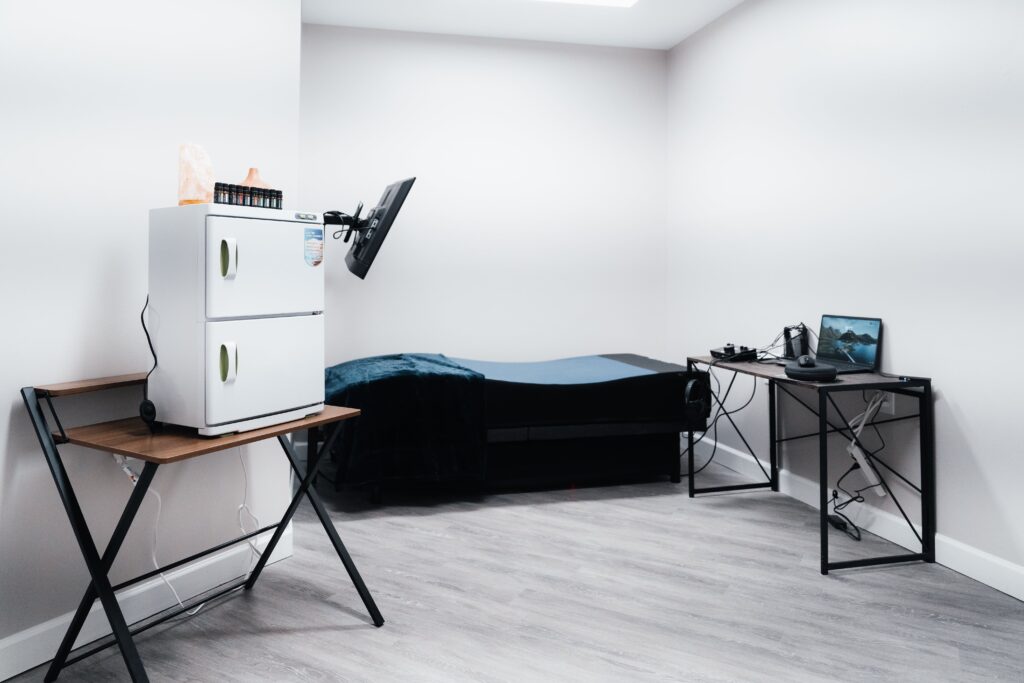
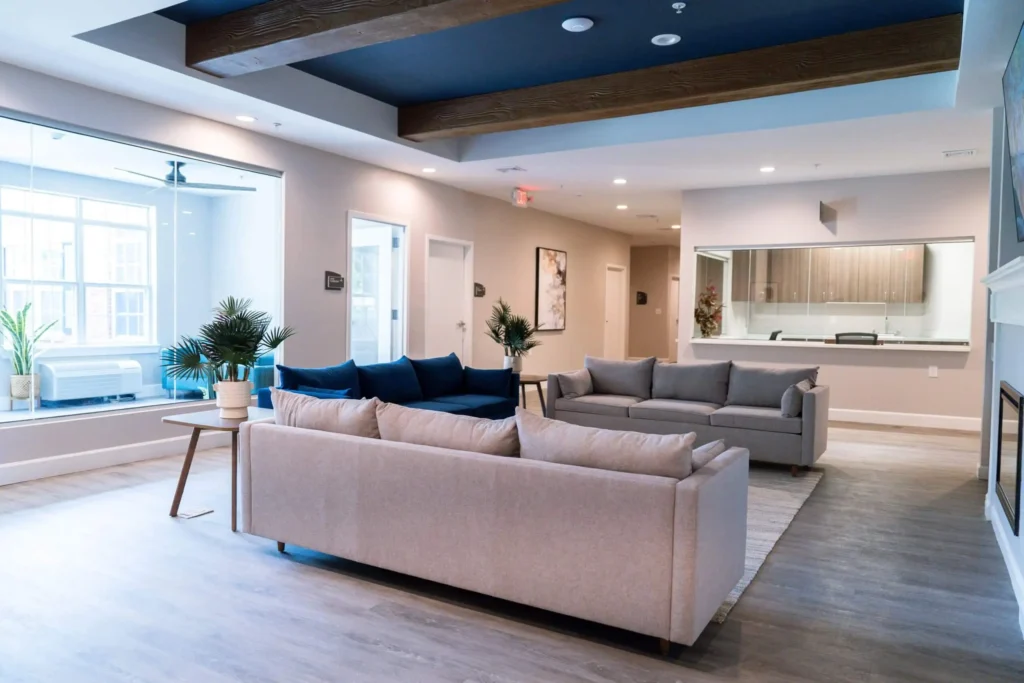
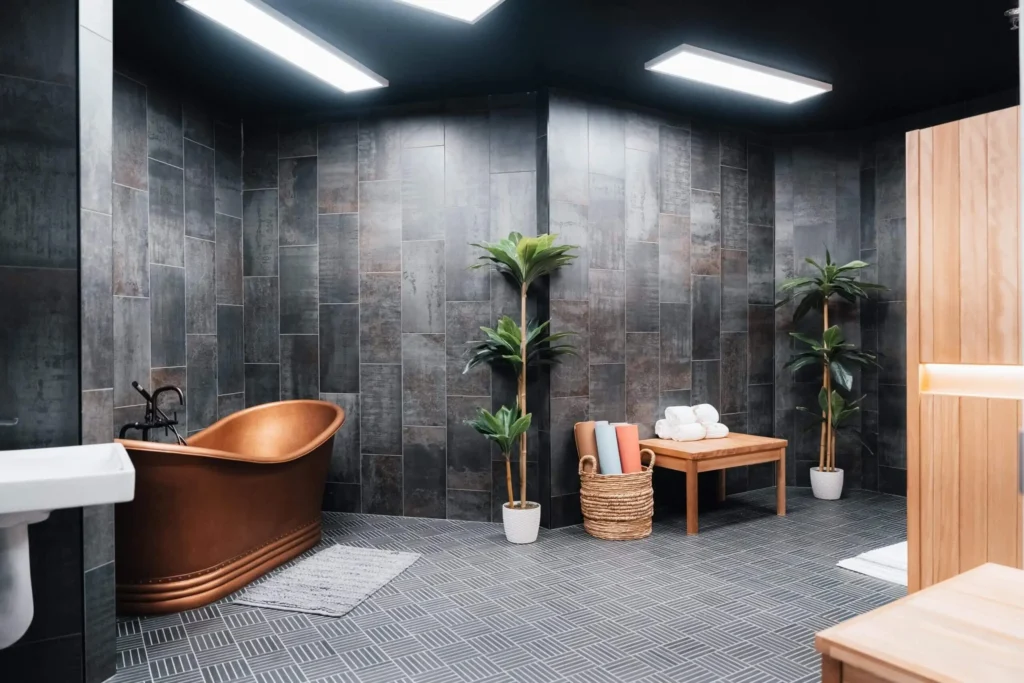
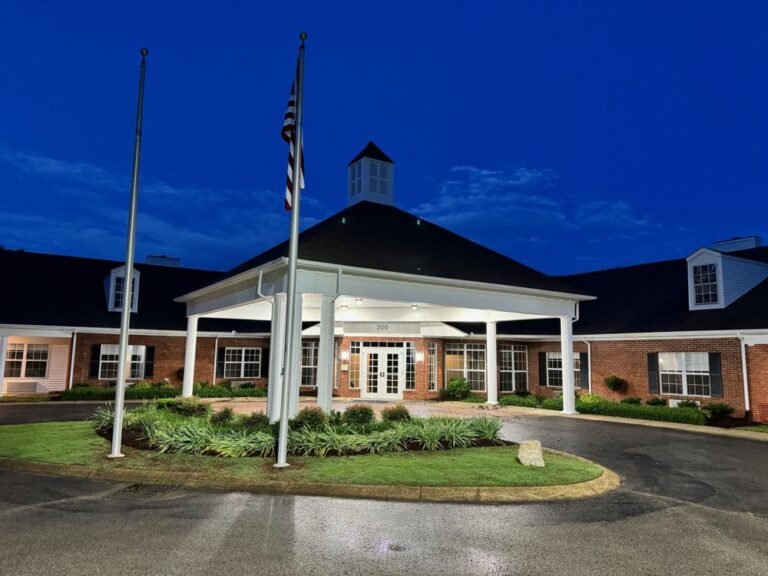
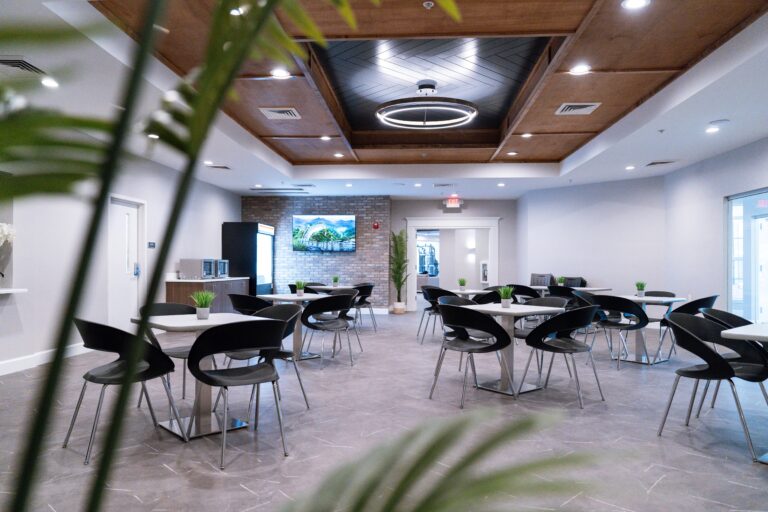
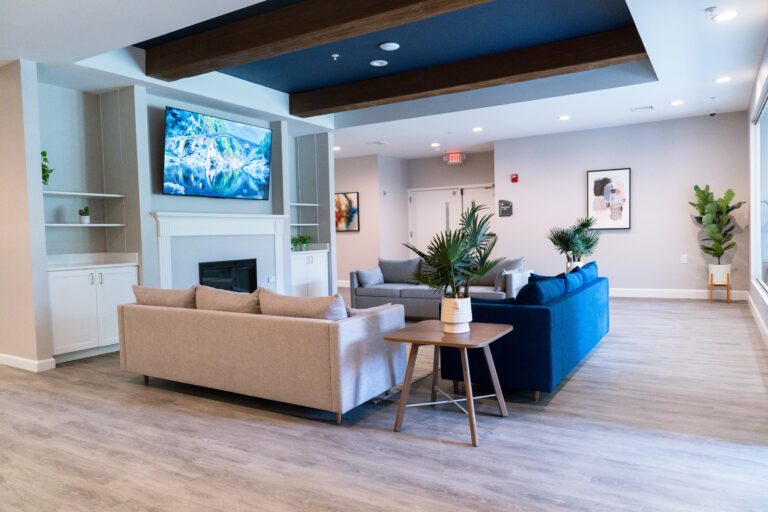
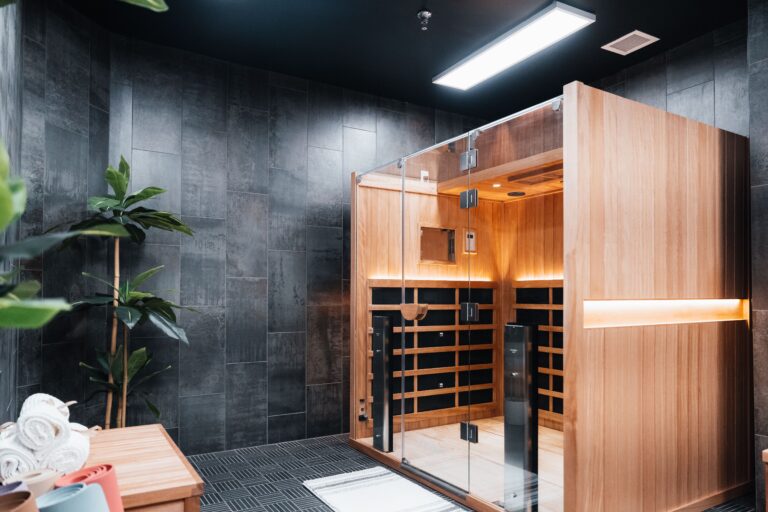
Tour Our Luxury Mental Health Facilities In NAshville
Arbor Wellness is a safe space where clients can feel comfortable, taken care of, and let down barriers as they go through the process of healing.
Our 30,000 sq. ft. mental health treatment center in Nashville offers a number of residential services and amenities that allow our clients to focus on their recovery without distraction. With access to a gym, ice bath, sauna, chef and more, we help our clients feel comfortable so they can focus on what matters most – healing.






Mental Health Disorders We Treat
Mental Health Treatment
Mental Health Disorders affect millions of people each day, diminishing their overall quality of life.
Dual Diagnosis Treatment
Dual Diagnosis happens when a person with a substance use disorder also has a mental health condition.
Anxiety Treatment
Anxiety is the most common mental illness in the United States and can be debilitating when left untreated.
Depression Treatment
Regardless of the type of depression a person has, it impacts how they view their world and leaves them living without hope.
Bipolar Disorder Treatment
Bipolar disorder, formerly called "manic-depression," is a debilitating disease that affects the lives of nearly 1 in every 100 people.
Self-Harm Treatment
Millions of people hurt themselves. Yet shame and guilt prevent these people from treatment that could improve their lives.

Combatting The Stigma of Mental Health
According to the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH), “mental illnesses are common in the United States, affecting tens of millions of people each year. Estimates suggest that only half of people with mental illnesses receive treatment.”
Here in Nashville, the stigma surrounding mental health doesn’t just prevent individuals from seeking professional help but can also impact those who do take the courageous step toward treatment.
Many of our Nashville clients initially arrive carrying feelings of shame and guilt that can inhibit them from fully engaging in the healing process.
We believe that Nashville residents deserve compassionate care that acknowledges both the universal and unique aspects of mental health challenges in our community.
In addition, here are some of the ways we combat the stigma of mental health:
A critical aspect of combatting mental health stigma involves empowering individuals in their treatment program. One of the best ways to empower clients is by offering choices to create an individualized treatment plan.
This empowers individuals to be in the driver’s seat of their treatment program. With our therapeutic services as well as varying levels of care, clients can create a program that works best for them.
In the past, mental health treatment models focused on determining what was “wrong” with the client. However, trauma-informed care practices consider how a person’s life experiences shaped them into who they are today. Therefore, it changes the focus of treatment from “What’s wrong with you?” to “What’s happened to you?”
As a result, our treatment team will screen for underlying trauma—which can be different for everyone.
The way people talk about mental health can reinforce stigma and stereotypes. This can even occur among peers in treatment—or the way clients talk about themselves during group or individual therapy sessions.
Stigmatizing language can lead to negative self-talk, affecting your self-image and self-esteem. At Arbor Wellness, we encourage clients to use empowering language and to call out stigmatizing words when they hear them.
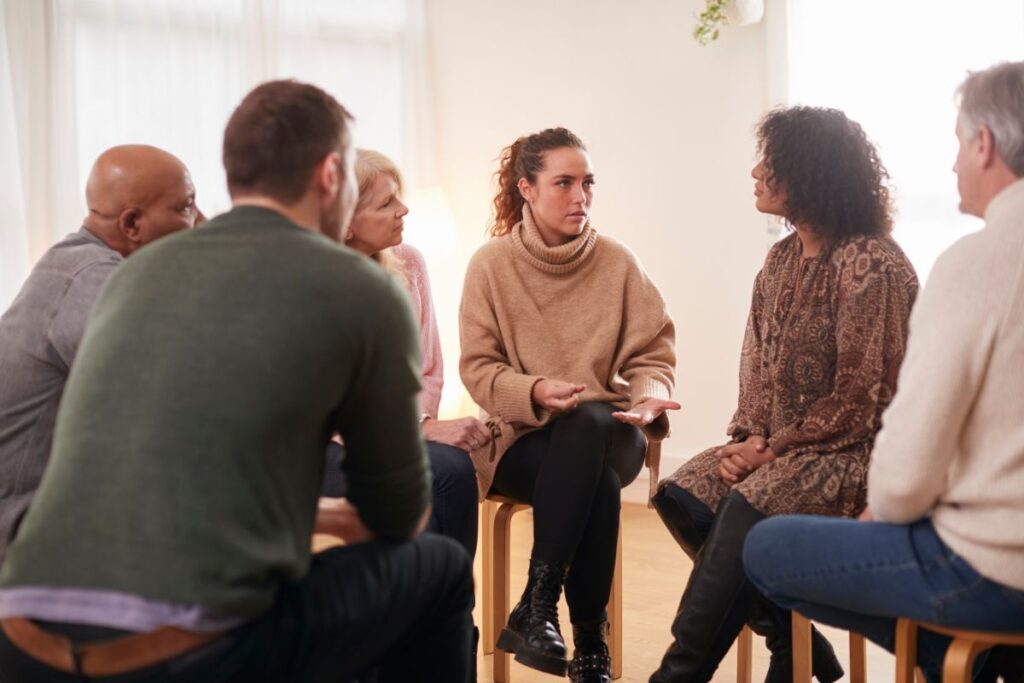
Compassion and empathy are critical to helping clients overcome the stigma of mental health disorders. This is crucial for both treatment professionals and peers. When clients display compassion and empathize with one another, they create an environment conducive to healing, safety, and recovery.
Oftentimes, family members struggle to understand—or accept—what their loved one is going through due to their disorder. Family involvement is critical to educating family members about mental health, treatment, and long-term recovery.
Our family therapy program helps clients build healthy relationships with their families.
Peer support is vital to creating a community of recovery and building connections with others who share similar experiences. Oftentimes, people with mental health disorders feel isolated and different from those around them.
However, peer support groups reduce stigma by helping clients build a recovery community that encourages acceptance and healing.
Clinically-Driven Therapeutic Modalities
Our clinical programming implements clinically driven therapeutic modalities that integrate trauma-informed principles, creating personalized treatment plans that address the unique needs of each client while recognizing the impact of past trauma on current functioning.
Holistic Therapy
Holistic Therapy
Individual Therapy
Individual Therapy
Somatic Therapy
Somatic Therapy
Arbor Wellness FAQ
Arbor Wellness offers residential treatment, partial hospitalization, and outpatient services for mental health at our Nashville, TN location.
Arbor Wellness work with most major insurance providers who cover out-of-network benefits, typically a PPO, POS or EPO policy. We also offer affordable cash pay rates for those who are not covered by health insurance. At this time we do not accept Medicaid or Medicare policies.
Please visit the What We Treat page to learn more about the different mental illnesses we treat at Arbor Wellness.
Yes. We have a dedicated admissions team standing by 24 hours a day, 7 days a week who can help guide you to the help you need for mental health.
You might need mental health treatment if you experience persistent feelings of sadness, anxiety, or hopelessness that interfere with your daily life and relationships. Additionally, if you notice significant changes in your behavior, sleep patterns, or appetite, it could be beneficial to seek professional help.
If you’re still unsure on whether or not to seek help, we offer comprehensive mental health self-assessments so you can better understand what your needs are:
Meet Our Expert Care Team
From our therapists to our chefs to our maintenance team, at Arbor Wellness, everyone here sees their work as part of something meaningful.
Our mental health professionals use treatments that science has proven to work, while also exploring new approaches that show promise. They believe in treating the whole person because they know everyone has the ability to heal.

Ashlyn Wright
Why Choose Arbor Wellness?
Arbor Wellness is not your typical mental health treatment program in Nashville. We offer a luxury, personalized treatment approach that allows each client to experience the therapies and modalities that work to achieve long-term recovery from mental illness. These are just a few reasons why our program is your best option when seeking mental health treatment in Nashville, Tennessee.

Personalized Solutions for Mental Health
Our customized approach allows each client a unique treatment experience that works on the core issues that are causing issues in their lives.

A Full Continuum of Care
From residential to partial hospitalization and outpatient therapy, Arbor Wellness offers a full continuum for best results in mental health treatment.

Master-Level Clinicians
The team at Arbor Wellness has been treating mental illness & co-occurring disorders for years. Our diverse and highly experienced staff utilize current and emerging evidence-based therapy modalities.

People who Trust Arbor Wellness
Don’t trust our word, let others share their experience, strength, and hope.
If You are in need of immediate assistance...
Don’t hesitate to contact us immediately. In the case of a medical emergency please contact 911 or visit your local emergency department.
Latest News & Articles
Stay up-to-date with all things mental health with our latest blog articles.
What Is Drug & Alcohol Detox? Symptoms & Timeline
- T Squared
- October 27, 2025
- Substance Use Disorder
Complex PTSD & Dissociation: Understanding the Mind's Protective Response
- arborwellnessm
- October 3, 2025
- Trauma
What Are The 7 Stages of Grief?
- Kristin Rivera, LCSW
- September 19, 2025
- Mental Health
Can Ozempic Cause Depression?
- Kristin Rivera, LCSW
- August 25, 2025
- Mental Health
Understanding Different Types of Treatment Centers
- Kristin Rivera, LCSW
- August 4, 2025
- Mental Health
How To Manage Severe Irritability
- Kristin Rivera, LCSW
- July 21, 2025
- Uncategorized